Using algae and fungi to create new biofuel systems
Scientists at Michigan State University have found a way for microorganisms to work together to increase the production of bio-oil.
New proof of this concept was published in the journal "Biotechnology for Biofuels". It is a biofuel production platform that uses two types of marine algae and soil fungi. It reduces the cost of planting and receiving, and improves productivity. These factors currently hinder the widespread use of biofuels.
Algae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and the fungus Mortierella can all produce oil that can be used by humans. For example, they can provide ingredients in products such as biofuels that power cars, as well as ingredients in omega-3 fatty acids that are good for heart health.
When scientists put these two organisms in the same environment, the tiny algae attached to the fungus to form large particles visible to the naked eye. This polymerization method is called biological flocculation.
When they are harvested together, these organisms produce more oil than they grow and harvest alone.
"We used natural organisms with strong mutual affinity," said Du Zhiyan, a research collaborator and assistant researcher in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. "Algae production is very high, and the fungus we use is neither toxic nor edible to us." This is a very common soil fungus that can be found in your backyard.
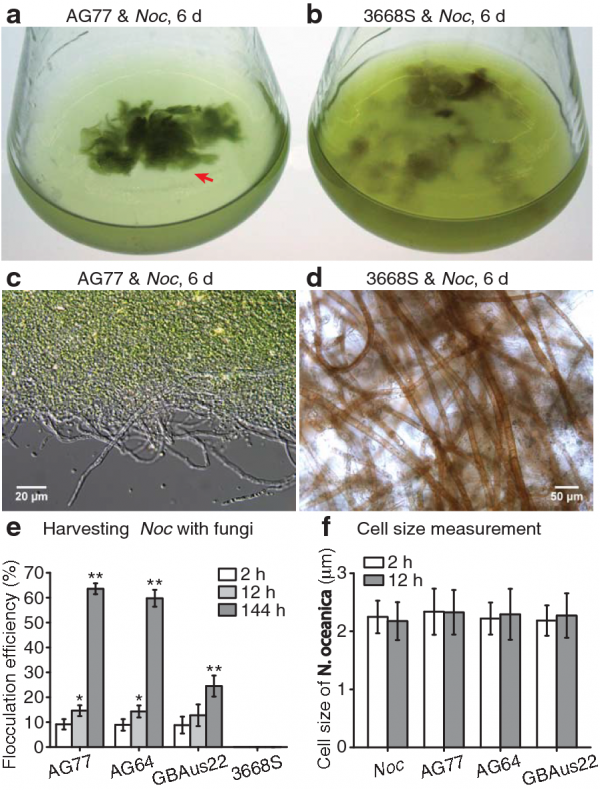
Experimental observation and data analysis
The researchers discussed other advantages of discovering biofuel systems, including:
-Sustainability because it does not rely on fossil fuels. Fungi grow on sewage or food debris, while algae grow in seawater.
-Cost savings, because large amounts of algae and fungi are easily captured with simple tools, such as a net.
-Easy to expand because these organisms are wild strains that have not been genetically modified. They do not pose a risk of infection in any environment they come into contact with.
The researchers also discussed how their findings solved two problems that hindered biofuel production.
Bioflocculation is a relatively new method. Biofuel systems often rely on a species, such as algae, but they are constrained by productivity and cost issues. The first problem arises because of the low oil production of systems that rely solely on algae.
"When algae growth is hindered by environmental stress (such as nitrogen deficiency), they can produce a lot of oil." The most popular method for algae oil in the laboratory is to cultivate cells to high density levels, and then centrifuge The washing method separates the cells from the nutrients, leaving the cells in starvation. "This method involves many steps, time and labor, and is not suitable for industrial-scale production."
This new method uses ammonia to feed algae, and ammonia is a source of nitrogen that algae can quickly use to grow. However, the supply of ammonia source is artificially controlled, so that the algae produce the maximum cell density and automatically enter the nitrogen starvation state. Close monitoring of nitrogen supply can increase bio-oil production and reduce costs.
The second problem is the high cost of oil recovery, because algae are small and difficult to collect. The cost of oil recovery may be as high as 50% of the cost of bio-oil production.
"Through biological flocculation, fungal and algal aggregates are easily harvested with simple, inexpensive tools," Du said.
Looking ahead, scientists hope to use this system to produce biofuels on a large scale. They also know the complete genomes of these two organisms and can use genetic engineering to further improve this method.
The research is currently being conducted in the laboratories of Christoph Benning and Gregory Bonito.
Original report: https://biotechnologyforbiofuels.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13068-018-1172-2
(Originally from: Biomass Magazine China New Energy Network Comprehensive)
Kn95 Respirator,Kn95 Filters 3D Mask,Kn95 5 Layers Cup Face Mask,Nonwoven Cloth Kn95 Face Mask
Jiangmen anjian biotechnology co. LTD , https://www.anjianmask.com